
The plant membranes are composed mainly of lipids which possess a hydrophilic, polar head attached to a glycerol backbone and a hydrophobic tail built of two fatty acids. Some of them are inevitable in the proper function of plant cells and some have positive effects on human health (e.g., anti-inflammatory, anticancer, antibacterial, and antiparasitic activity ) or are demanded in the different branches of industry, like food, pharmaceuticals, and cosmetics production. Nowadays, structure and role of about 400 different fatty acids are known in the plant kingdom. Therefore, it is worth to present the selected lipid issues with the aim of explaining differences in their content, specific role in plants and emphasizing their impact in adverse conditions. These differences could be partially explained by the quantitative and qualitative changes in the lipid composition, which in turn triggers membrane fluidity and its function. , whereas others are less sensitive to temperature fluctuations, e.g., Arabidopsis thaliana L. For example, some of the plants are sensitive to temperature changes, e.g., Cucumis sativa L. Among them are alterations in the content of lipids, proteins or other molecules. In order to maintain the normal physiological function and survive in the unfavorable environmental conditions, plants have developed defense mechanisms. They have to adapt to the external changes like humidity, salinity, or temperature. Plants are constantly exposed to stress resulting from the conditions in which they are growing. The key advantage of lipid research was the conclusion that lipids could serve as the markers of plant physiological condition and the detailed knowledge on lipids chemistry will allow to modify their composition for industrial needs. High level of lipids remodeling in the plant membranes under different environmental conditions, e.g., nutrient deficiency, temperature stress, salinity or drought was proved. Moreover, in order to better understand the biomembranes remodeling, the model (artificial) membranes, mimicking the naturally occurring membranes are employed and the survey on their composition and application in different kind of research was performed. The involvement of lipids in xantophyll cycle and glycerolipids synthesis (as the most abundant of all lipid classes) were also discussed. Then, classification, composition, role, and organization of lipids were displayed.

Classification, nomenclature, and abundance of fatty acids was discussed.
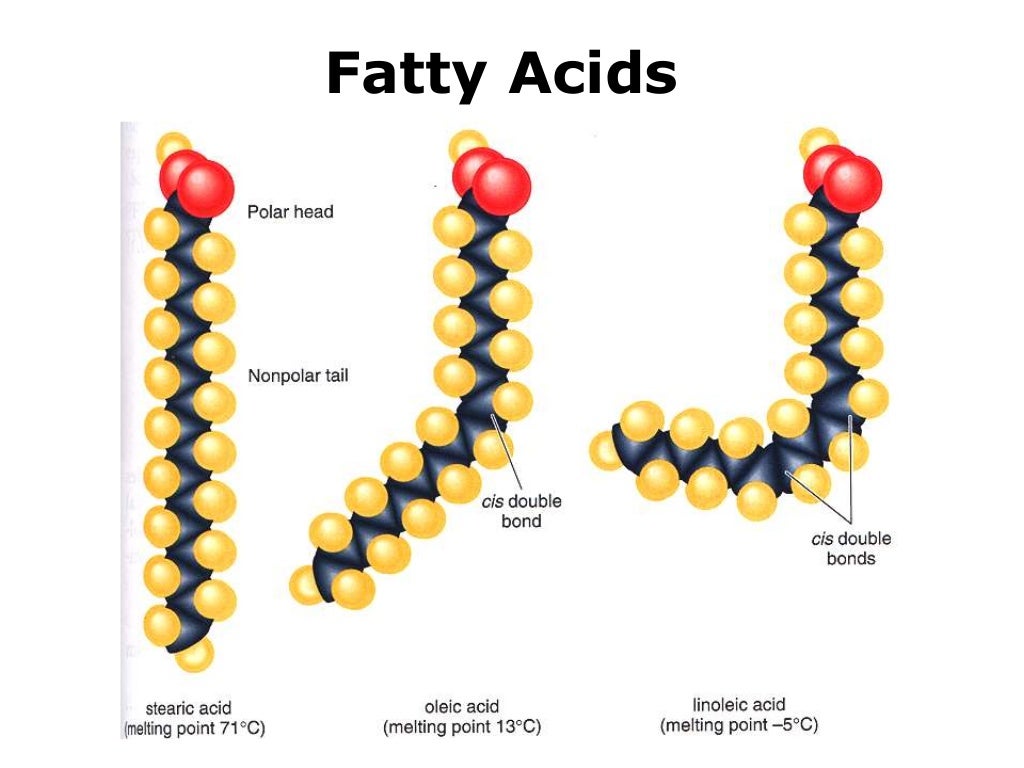
The paper focuses on the selected plant lipid issues.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
